


Next: Accretion Rate
Up: Free-fall Time
Previous: Problem
Contents
Solve equation (2.16) and obtain equations (2.23)
and (2.24).
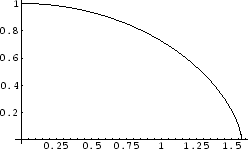
Figure:
Free-fall. x-axis and y-axis represent 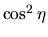 and
and
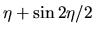 .
.
 |
In the present case,
at 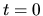 , since
, since 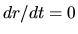 the energy is negative.
Equation (2.19) shows us
the energy is negative.
Equation (2.19) shows us
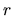 becomes equal to zero (the gas collapses) if
becomes equal to zero (the gas collapses) if 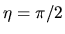 as well as
as well as 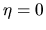 at
at 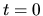 .
Equation (2.21) indicates
it occurs at the epoch of
.
Equation (2.21) indicates
it occurs at the epoch of
where 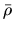 represents the average density
inside of
represents the average density
inside of 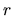 , that is
, that is
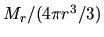 .
This is called ``free-fall time'' of the gas.
This gives the time-scale for the gas with density
.
This is called ``free-fall time'' of the gas.
This gives the time-scale for the gas with density 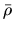 to collapse.
In the actual interstellar space,
the gas pressure is not negligible.
However,
to collapse.
In the actual interstellar space,
the gas pressure is not negligible.
However, 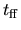 gives a typical time-scale for a gas cloud
to collapse and to form stars in it.
gives a typical time-scale for a gas cloud
to collapse and to form stars in it.



Next: Accretion Rate
Up: Free-fall Time
Previous: Problem
Contents
Kohji Tomisaka
2007-07-08
