


Next: Isotharmal shock
Up: Shock Wave
Previous: Shock Wave
Contents
Passing through a shock front moving with a speed 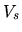 , the physical variables
, the physical variables 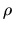 ,
, 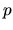 , and
, and 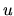 change abruptly.
Since the basic equations of hydrodynamics is unchanged after chosing a system moving
change abruptly.
Since the basic equations of hydrodynamics is unchanged after chosing a system moving 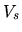 ,
the continuity equation
,
the continuity equation
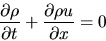 |
(A.26) |
gives an equation for a steady state as
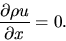 |
(A.27) |
Considering a region containing the shock front at 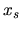 which extends from
which extends from
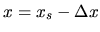 to
to
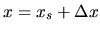 and integrating the above equation, we get
and integrating the above equation, we get
![\begin{displaymath}
\int_{x_s-\Delta x}^{x_s+\Delta x}\frac{d \rho u}{d x}dx=
\left[\rho u\right]_{x_s-\Delta x}^{x_s+\Delta x}.
\end{displaymath}](img1488.png) |
(A.28) |
Thus, we obtain the jump condition conserning the mass coservation as
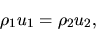 |
(A.29) |
where the quatities with suffix 1 are for preshock and those with suffix 2 are for postshock.
Equation of motion for steady state
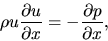 |
(A.30) |
gives
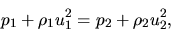 |
(A.31) |
where we used equation(A.29).
Subsections



Next: Isotharmal shock
Up: Shock Wave
Previous: Shock Wave
Contents
Kohji Tomisaka
2007-11-02
![]() , the physical variables
, the physical variables ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() change abruptly.
Since the basic equations of hydrodynamics is unchanged after chosing a system moving
change abruptly.
Since the basic equations of hydrodynamics is unchanged after chosing a system moving ![]() ,
the continuity equation
,
the continuity equation