X-factor
Since the H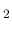 molecule is the homonuclear diatomic molecule,
the H
molecule is the homonuclear diatomic molecule,
the H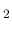 molecule has no electric dipole.
Thus, the electric dipole radiation is not expected for this molecule.
While the second abundant molecule CO is the heteronuclear diatomic
molecules and has electric dipole.
Lower levels of rotational transition of CO are
relatively easily excited even in the cold interstellar medium of
molecule has no electric dipole.
Thus, the electric dipole radiation is not expected for this molecule.
While the second abundant molecule CO is the heteronuclear diatomic
molecules and has electric dipole.
Lower levels of rotational transition of CO are
relatively easily excited even in the cold interstellar medium of
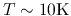 .
Therefore, the rotational transition of CO molecule is the first
possibility to observe cold molecular gas.
The
.
Therefore, the rotational transition of CO molecule is the first
possibility to observe cold molecular gas.
The 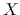 -factor represents the ratio of the column density of H
-factor represents the ratio of the column density of H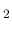 molecules
molecules 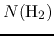 to the integrated intensity of
to the integrated intensity of 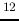 CO line
CO line
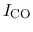 as
as
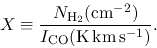 |
(F.1) |
There are several empirical but physical estimations of the 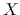 -factor:
Using
-factor:
Using 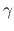 -rays,
-rays, 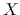 -factor is estimated as
-factor is estimated as
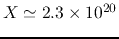 (Strong et al. 1988).
This is based on the idea that the emissivity of
(Strong et al. 1988).
This is based on the idea that the emissivity of  -ray emission
is proportional to the cosmic-ray intensity times the number of
target nuclei.
The
-ray emission
is proportional to the cosmic-ray intensity times the number of
target nuclei.
The  -ray intensity is proportional to the column density
if the cosmic-ray intensity is uniform.
From the distribution of
-ray intensity is proportional to the column density
if the cosmic-ray intensity is uniform.
From the distribution of  -ray intensity,
Strong et al. (1988). estimated total column density
-ray intensity,
Strong et al. (1988). estimated total column density
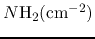 using some model.
This gives the value of
using some model.
This gives the value of 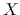 -factor.
-factor.
Estimations using the Virial mass of the interstellar cloud
and the visual extinction 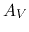 .
.
Kohji Tomisaka
2012-10-03
![]() .
.