- ... Formation1
- http://yso.mtk.nao.ac.jp/~tomisaka/Lecture_Notes/StarFormation/3.pdf
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... them4.1
-
One of the reasons why large increase in the mass/flux ratio is favored is understood as follows:
There have been a long-standing ``magnetic flux problem of stars'' in which
the magnetic flux of, say,
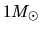 main-sequence star
main-sequence star
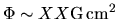 is much smaller
than that of the parent cloud
is much smaller
than that of the parent cloud
 .
The magnetic flux must be reduced in the star formation process.
If the mass-flux ratio increases much in these density range, this might resolve
the magnetic flux problem of stars.
.
The magnetic flux must be reduced in the star formation process.
If the mass-flux ratio increases much in these density range, this might resolve
the magnetic flux problem of stars.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...)
4.2
- This means
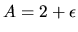 and
and 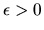 and
and 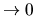
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... stateC.1
- Reference book
for this appendix is chapter 4 of Chandrasekhar (1939).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.