


Next: Problem 1
Up: Local Star Formation Process
Previous: Local Star Formation Process
Contents
Consider a hydrostatic balance of isothermal cloud.
By the gas density, 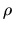 , the isothermal sound speed,
, the isothermal sound speed, 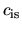 , and the gravitational potential,
, and the gravitational potential,
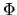 , the force balance is written as
, the force balance is written as
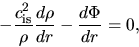 |
(4.1) |
and the gravity is calculated from a density distribution as
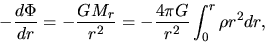 |
(4.2) |
for a spherical symmetric cloud, where 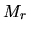 represents the mass contained inside the radius
represents the mass contained inside the radius 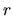 .
The expression for a cylindrical cloud is
.
The expression for a cylindrical cloud is
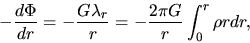 |
(4.3) |
where 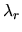 represents the mass per unit length within a cylinder of radius being
represents the mass per unit length within a cylinder of radius being 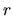 .
.
For the spherical symmetric case, the equation becomes the Lane-Emden equation with the polytropic index of
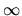 (see Appendix C.1).
This has no analytic solutions.
However, the numerical integration gives us a solution shown in Figure 4.1 (left).
Only in a limiting case with the infinite central density, the solution is expressed as
(see Appendix C.1).
This has no analytic solutions.
However, the numerical integration gives us a solution shown in Figure 4.1 (left).
Only in a limiting case with the infinite central density, the solution is expressed as
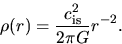 |
(4.4) |
Increasing the central density, the solution reaches the above Singular Isothermal Sphere (SIS) solution.
On the other hand, a cylindrical cloud has an analytic solution (Ostriker 1964) as
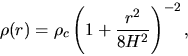 |
(4.5) |
where
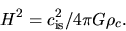 |
(4.6) |
Far from the cloud symmetric axis, the distribution of equation (4.5) gives
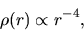 |
(4.7) |
while the spherical symmetric cloud has
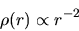 |
(4.8) |
distribution.
Subsections



Next: Problem 1
Up: Local Star Formation Process
Previous: Local Star Formation Process
Contents
Kohji Tomisaka
2007-11-02
![]() , the isothermal sound speed,
, the isothermal sound speed, ![]() , and the gravitational potential,
, and the gravitational potential,
![]() , the force balance is written as
, the force balance is written as
![]() (see Appendix C.1).
This has no analytic solutions.
However, the numerical integration gives us a solution shown in Figure 4.1 (left).
Only in a limiting case with the infinite central density, the solution is expressed as
(see Appendix C.1).
This has no analytic solutions.
However, the numerical integration gives us a solution shown in Figure 4.1 (left).
Only in a limiting case with the infinite central density, the solution is expressed as